안녕하세요,
인공지능 전공자라면 정말 중요하지만 어렵게 느끼는 선형대수학 입니다.
오늘은 MIT GilbertStrang 교수님의 2강인 An Overview of Linear Algebra 에 대해 리뷰해보겠습니다.
This is an overview of linear algebra given at the start of a course on the math ematics of engineering.
Vectors
What do we do with vectors? Take combinations

We can multiply vectors by scalars(such as under x1,x2,x3), add, and subtract. Given vectors u, v
and w we can form the linear combination x1u + x2v + x3w = b.

The collection of all multiples of u forms a line through the origin. The collec tion of all multiples of v forms another line. The collection of all combinations of u and v forms a plane. Taking all combinations of some vectors creates a subspace.
We could continue like this, or we can use a matrix to add in all multiples of w.
Matrices
Create a matrix A with vectors u, v and w in its columns:
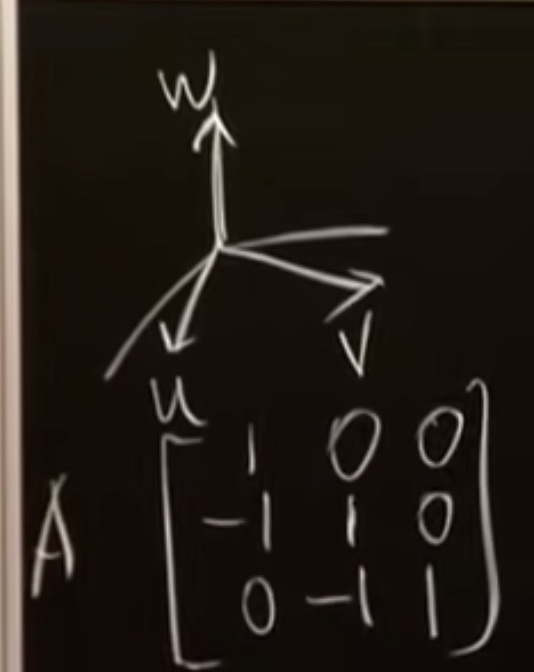
A times x very important of matrix times a vector.

This particular matrix A is a dif ference matrix because the components of Ax are differences of the components of that vector.

When we say x1u + x2v + x3w = b we’re thinking about multiplying num bers by vectors; when we say Ax = b we’re thinking about multiplying a matrix (whose columns are u, v and w) by the numbers. The calculations are the same, but our perspective has changed.
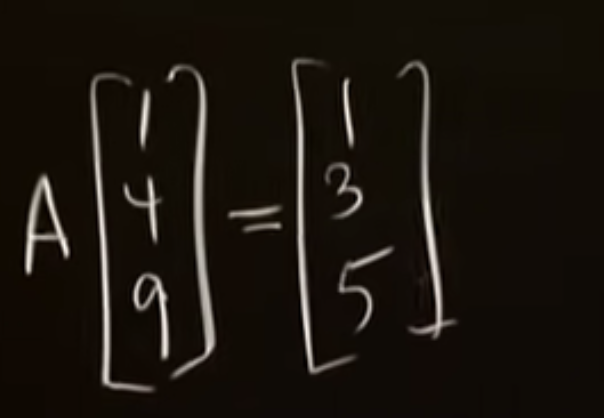
For any input vector x, the output of the operation “multiplication by A” is some vector b
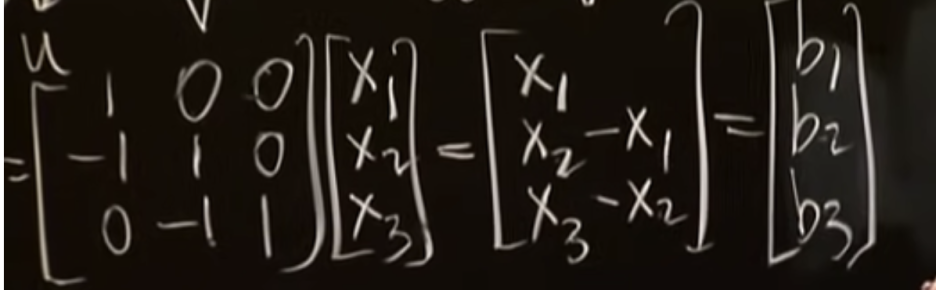
A deeper question is to start with a vector b and ask “for what vectors x does Ax = b?” In our example, this means solving three equations in three un knowns.

This is the solution.
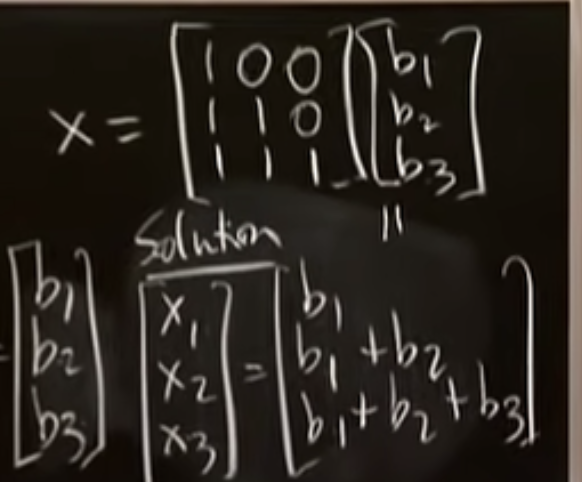
It`s a matrix times b. Ax = b or x = A−1b. If the matrix A is invertible, we can multiply on both sides by A−1 to find the unique solution x to Ax = b.
Second example has the same columns u and v and replaces column vector w:
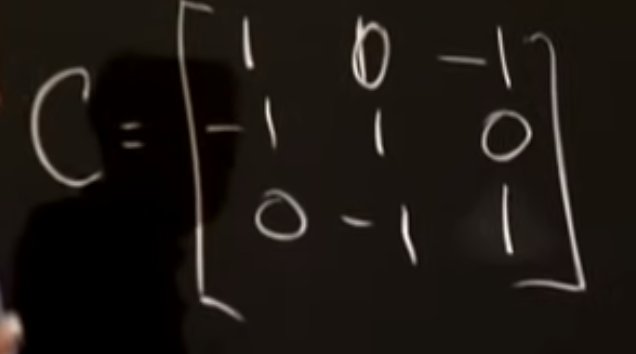
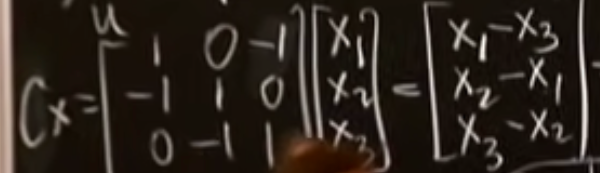
Our system of three equations in three unknowns becomes circular.
Where before Ax = 0 implied x = 0, there are non-zero vectors x for which Cx = 0. Foranyvectorxwithx1 = x2 = x3,Cx = 0. This is asignificant difference; we can’t multiply both sides of Cx = 0 by an inverse to find a non zero solution x.
The system of equations encoded in Cx = b is : (under picture)
Add these eaquations together, we get : (under picture)
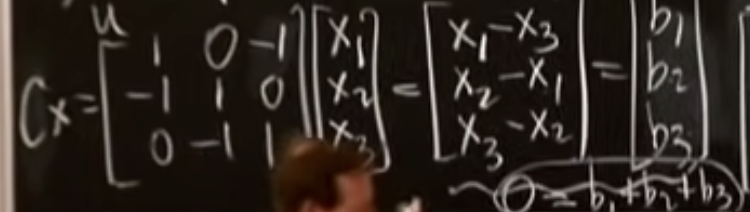
This tells us that Cx = b has a solution x only when the components of b sum to 0.
In a physical system, this might tell us that the system is stable as long as the forces on it are balanced.
There are some troubles. So let`s see geometrically why were in trouble.
Geometrically, the columns of C lie in the same plane (they are dependent; the columns of A are independent).
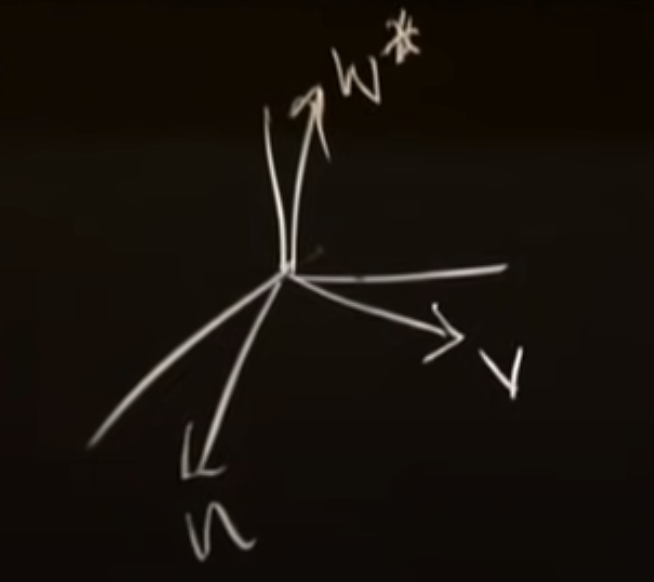
Did not change u and v but I changed only w to minus one.
what does this mean?
Minus one sort of going zero, one is the z direction.
w star is a different w.
all combinations of u, v, and the third guy w*.
This matrix is not invertible, those three vectors are not a basis.
Their combinations are only in a plance(plane would be a typical subspace).
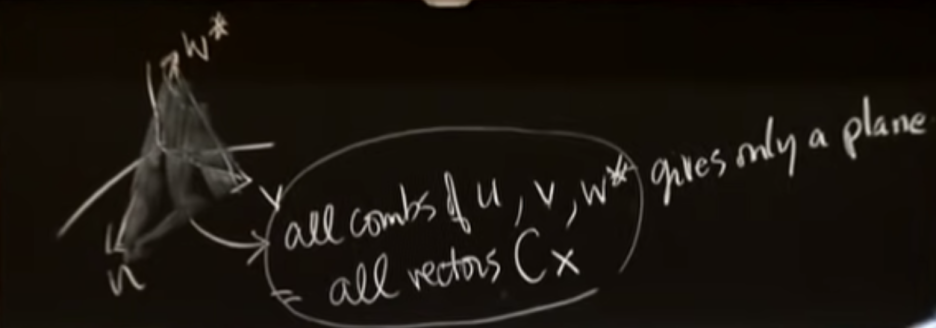
Subspaces

Can we describe what vectors we get?
What b`s do we get? We do not get them all
We only get a plane of them. We get the ones where the components add to zero.
A vector space is a collection of vectors that is closed under linear combinations.
A subspace could be equal to the space it’s contained in; the smallest subspace contains only the zero vector.
What is the smallest subspace of R^3?
1. the origin
2. a line through the origin
3. a plane through the origin
4. all of R^3.
Conclusion
When you look at a matrix, try to see “what is it doing?”
Matrices can be rectangular; we can have seven equations in three unknowns.
Rectangular matrices are not invertible, but the symmetric, square matrix AT A that often appears when studying rectangular matrices may be invertible.
오늘은 MIT 길버트스트랭 교수님의 선형대수학 2강에 대해 리뷰해보았습니다.
다음에는 3강으로 리뷰해보겠습니다.
'7. 수학공부 > 선형대수학' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Lecture5 Transposes, Permutations, Vector Spaces (2) | 2024.11.26 |
|---|---|
| Lecture #4 Factorization into A = LU (0) | 2024.11.24 |
| Lecture#3 Multiplication and Inverse Matrices (0) | 2024.11.23 |
| Lecture #2. Elimination with Matrices (1) | 2024.11.22 |
| 1. The Geometry of Linear Equations (1) | 2024.11.16 |