안녕하세요,
오늘은 MIT Gilbert Strang 교수님의 선형대수학 Lecture12 Graphs, Networks, Incidence Matrices에 대해 학습하겠습니다.

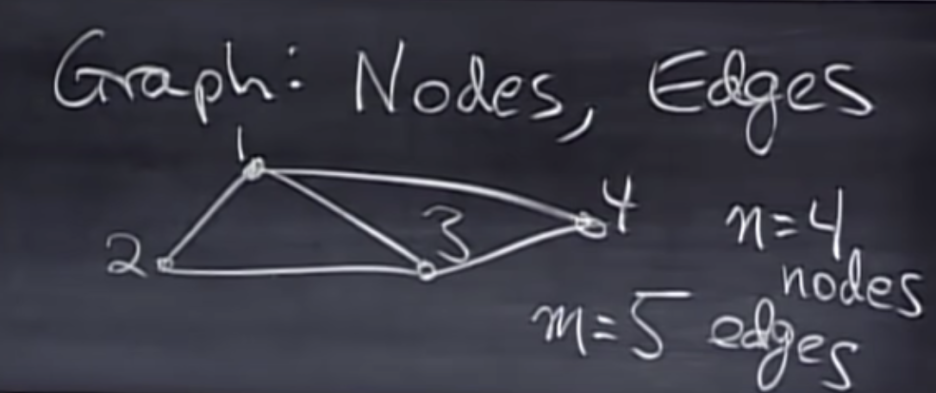
Graph : Nodes, Edge
그래프는 꼭짓점인 Node와 변인 Edge로 구성되어 있다.
아래의 그래프는 꼭짓점 4개 (N=4), 변 5개(M=5)로 이루어져 있다.
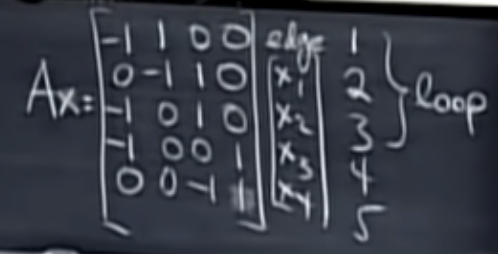
Incidence Matrix (근접행렬)
The incidence matrix of this directed graph has one column for each node of the graph and one row for each edge of the graph
꼭짓점인 Node의 개수를 column으로, 변인 Edge의 개수를 row로 만들어 5*4 근접행렬을 만들 수 있다.
If an edge runs from node a to node b, the row corresponding to that edge has −1 in column a and 1 in column b; all other entries in that row are 0.
변은 노드 a로부터 노드 b 까지 이동한다면, 출발점인 a를 -1, 끝점인 b를 1로 지정한다. 다른 entries는 0이다.
Node1은 Node2와 3으로 연결되어 있고, Node 2는 Node 3과 연결되어 있다.
Loop (노드들이 연결되어 있는 그래프, Linearly dependent하다.)
Note that nodes 1, 2 and 3 and edges 1, 2 and 3 form a loop.
노드 1,2,3과 엣지 1,2,3은 Loop를 형성한다..
Note that the third row is the sum of the first two rows; loops in the graph correspond to linearly dependent rows of the matrix.
두개의 행(row)의 합이 세번째 행(row 3)이다.따라서, 그래프의 Loop는 Linearly dependent(선형종속)이다.
If the components xi of the vector x describe the electrical potential at the nodes i of the graph, then Ax is a vector describing the difference in potential across each edge of the graph.
Vector x의 성분 xi가 그래프의 노드 i에서 전기전압(electrical potential) 관점으로 설명한다면, Ax는 그래프의 각 노드에서 전압(potential)의 차이를 설명하는 vector이다.
즉, Vector x는 node에서의 전압(potential)이다.
We see Ax=0 when x1 =x2 =x3 =x4, so the nullspace has dimension 1.
x1 = x2 = x3 = x4일 때, Ax = 0 이므로 nullpace 의 차원은 1이다.
In terms of an electrical network, the potential difference is zero on each edge if each node has the same potential. If one node of the network is grounded then its potential is zero.
전자회로에서, 각 노드들의 전압이 같다면 전위차(potential differences)는 0이다. 네트워크의 한 노드라도 접지되어 있으면 전압은 0이다.
The matrix has 4 columns and a 1 dimensional nullspace, so its rank is 3. The first, second and fourth columns are its pivot columns; these edges connect all the nodes of the graph without forming a loop – a graph with no loops is called a tree.
행렬은 4개의 column과 1차원 nullspace를 가지고 있으므로 rank는 3이다. 1,2,3,4열들은 pivot columns(회전하는 열)이고, 이 edges들은 loop를 형성하지 않고 그래프의 모든 node들을 연결한다.
그리고, Loop가 없는 graph를 tree라고 한다.

AT y = 0.
Since AT has 5 columns and rank 3 we know that the dimension of N(AT) is m − r = 2.
AT는 column 5와 rank 3을 가지고 있으므로, 차원은 5-3인 2이다.
Note that 2 is the number of loops in the graph and m is the number of edges. The rank r is n − 1, one less than the number of nodes. This gives us # loops = # edges − (# nodes − 1)
2는 loop의 수이고 M은 edge의 수이다. r(rank)는 n-1로 노드 수보다 1개 적다.
위의 내용을 공식으로 쓰면 Euler`s formula가 된다.


Kirchhoff`s law
Vectors in the nullspace of AT correspond to collections of currents that satisfy Kirchhoff’s law.
AT의 nullspace에 있는 vector는 Kirchhoff’s law을 만족하는 전류의 집합에 해당한다. 즉, nullspace는 키르히호프의 전기회로 법칙이다. 전기회로 1법칙은 전류가 하르는 길에서 들어오는 전류와 나가는 전류의 합이 같다.

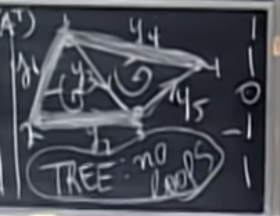
아래는 전기회로에 대한 그래프 모델이다.

정리
Incidence Matrix (근접행렬) : 꼭짓점인 Node의 개수를 column으로, 변인 Edge의 개수를 row로 근접행렬을 만들 수 있다.
Loop : 노드들이 연결되어 있는 그래프, Linearly dependent하다.
Node, Edge, Loop의 관계 : # loops = # edges − (# nodes − 1)
Rank : nodes -1
Euler 공식 : number of nodes − number of edges + number of loops = 1.
'7. 수학공부 > 선형대수학' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Lecture15 Projections onto Subspaces (2) | 2024.12.19 |
|---|---|
| Lecture14 Orthogonal Vectors and Subspaces (0) | 2024.12.17 |
| Lecture11 Matrix Spaces; Rank 1; Small World Graphs (2) | 2024.12.12 |
| Lecture10 The Four Fundamental Subspaces (1) | 2024.12.11 |
| Lecture9 Independence, Basis and Dimension (1) | 2024.12.10 |