MIT Gilberstrang 교수님의 Linear Algebra 15강 Projections onto Subspaces 강의

Projections (투영) : 하나의 vector를 다른 vector로 옮겨 표현하는 것
We can see from Figure 1 that this closest point p is at the intersection formed by a line through b that is orthogonal to a. If we think of p as an approximation of b, then the length of e = b − p is the error in that approximation. We could try to find p using trigonometry or calculus, but it’s easier to use linear algebra.
점 p는 a와 직교(orthogonal)하는 b를 지나는 선과 교점에 있다. 점 p는 b와 가장 가까운 곳이라고 생각한다면 e = b - p의 길이는 근사 식에서의 오차이다. 또한, 선형대수학을 이용하는 것이 p의 값을 구하는 가장 쉬운 방법이다.
* 벡터 b,e,p는 직각삼각형을 이룬다.

Projection matrix(투영 행렬)
Note that aaT is a three by three matrix, not a number; matrix multiplication is not commutative.
aaT는 숫자가 아닌 3 x 3 행렬이며, 행렬 곱셈은 commutative 하지 않다.
row vector와 column vector순으로 곱하면 상수가 되므로 P는 행렬이 되고 벡터 b를 벡터 a에 투영시키는 Projection matrix이다.
The column space of P is spanned by a because for any b, Pb lies on the line determined by a. The rank of P is 1. P is symmetric.
P의 column space는 a에 의해 span 된다. P의 rank는 1이며, 대칭행렬이고, P2 =P 이다.


Why project?
The equation Ax = b may have no solution. we project b onto a vector p in the column space of A and solve Axˆ = p.
방정식 Ax = b가 해를 갖지 않는 경우, Axˆ = p라는 근접한 해를 찾기 위해서이다.

In R3, how do we project a vector b onto the closest point p in a plane?
If a1 and a2 form a basis for the plane, then that plane is the column space of the matrix A = [ a1 a2 ]. There are many ways to show that e = b−p = b−Axˆ is orthogonal
R3에서 벡터 b를 평면에서 가장 가까운 점 p에 투영하는 방법은 아래와 같다. a1과 a2가 평면의 기저를 이룬다면, 그 평면은 행렬 A = [a1 a2]의 열 공간이다. e = b-p = b-Ax ˆ는 수직이다.
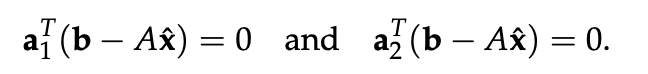

Note that e = b − Axˆ is in the nullspace of AT and so is in the left nullspace of A.
오차벡터 e = b - Ax ˆ는 AT 의 nullspace에 있고, 행렬 A의 left nullspace 에도 있다.
아래는 해를 구하는 방법으로, 단위 행렬이 되었다.
but if A isn’t a square matrix we can’t say that (ATA)−1 = A−1(AT)−1.
아래의 전개식을 할 수 있는 2가지 조건은 matrix A가 정방행렬 & 역행렬이 존재하는 경우이다.


정리
Projections (투영) : 하나의 vector를 다른 vector로 옮겨 표현하는 것
Projection matrix : row vector와 column vector순으로 곱하면 상수가 되므로 P는 행렬이 되고 벡터 b를 벡터 a에 투영시킨다.
Why Projection ? 정식 Ax = b가 해를 갖지 않는 경우, Axˆ = p라는 근접한 해를 찾기 위해서이다.
'7. 수학공부 > 선형대수학' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Lecture17 Orthogonal Matrices and Gram-Schmidt (0) | 2024.12.25 |
|---|---|
| Lecture16 Projection Matrices and Least Squares (1) | 2024.12.24 |
| Lecture14 Orthogonal Vectors and Subspaces (0) | 2024.12.17 |
| Lecture12 Graphs, Networks, Incidence Matrices (0) | 2024.12.14 |
| Lecture11 Matrix Spaces; Rank 1; Small World Graphs (0) | 2024.12.12 |